文章源自玩技e族-https://www.playezu.com/26311.html
文章源自玩技e族-https://www.playezu.com/26311.html
1. abs()函数返回数字的绝对值。文章源自玩技e族-https://www.playezu.com/26311.html
print( abs(-45) ) # 返回 45
print("abs(0.2):",abs(0.2)) # 返回 abs(0.2): 0.2
2. all() 函数用于判断给定的参数中的所有元素是否都为 true,如果是返回 true,否则返回 false。元素除了是 0、空、none、false 外都算 true;空元组、空列表返回值为true。文章源自玩技e族-https://www.playezu.com/26311.html
print( all( [0.1,1,-1] ) ) # 返回 true print( all( (none,1) ) ) # 返回 false(其中一个元素为none) print( all( [0,1,-1] ) ) # 返回 false(其中一个元素为0) print( all( [" ","a",""] ) ) # 返回 false(第三个元素为空)
3. any() 函数用于判断给定的参数是否全部为false,是则返回false,如果有一个为true,则返回true。 元素除了是 0、空、false外都算 true。文章源自玩技e族-https://www.playezu.com/26311.html
# 参数全部不为 0、空、false
print(any("-45")) # true
print(any(["-45"])) # true
print( any( ("0","ab","") ) ) # true(注意:第一个参数0加了双引号,表示为一个字符串)
# 参数全部为 0、空、false
print( any( (0,"") ) ) # false
print( any( (0,"",false) ) ) # false
4. bin()函数返回一个整数int或者长整数long int的二进制表示。文章源自玩技e族-https://www.playezu.com/26311.html
print( bin(10) ) # 0b1010 print( bin(133) ) # 0b10000101
5. bool() 函数用于将给定参数转换为布尔类型,如果参数不为空或不为0,返回true;参数为0或没有参数,返回false。文章源自玩技e族-https://www.playezu.com/26311.html
print( bool(10) ) # true print( bool([0]) ) # true print( bool(["123","s",0]) ) # true print( bool(0) ) # false print( bool() ) # false
6. bytearray()方法返回一个新字节数组。这个数组里的元素是可变的,并且每个元素的值范围: 0 <= x < 256(即0-255)。即bytearray()是可修改的二进制字节格式。文章源自玩技e族-https://www.playezu.com/26311.html
1 b = bytearray("abcd",encoding="utf-8")
2 print(b[0]) # 返回数字97,即把“abcd”的“a"对应的ascii码打印出来了
3 b[0] = 99 # 把字符串第一个字节修改为99(即对应字母为“c”)
4 print(b) # 返回:bytearray(b'cbcd')---第一个字节a已被修改为c
7. callable()函数用于检查一个对象是否可调用的。对于函数、方法、lambda函式、类以及实现了 __call__ 方法的类实例, 它都返回 true。(可以加括号的都可以调用)文章源自玩技e族-https://www.playezu.com/26311.html
1 def sayhi():pass # 先定义一个函数sayhi() 2 print( callable( sayhi ) ) # true
1 a = 1 2 print( callable( a ) ) # false
8. chr()函数用一个范围在range(256)内(即0~255)的整数作参数,返回一个对应的ascii数值。文章源自玩技e族-https://www.playezu.com/26311.html
# 把数字98在ascii码中对应的字符打印出来 print( chr(98) ) # 返回:b
9. dict()函数用来将元组/列表转换为字典格式。文章源自玩技e族-https://www.playezu.com/26311.html
print(dict(a='a', b='b', t='t'))
# 返回:{'b': 'b', 'a': 'a', 't': 't'}
print(dict( [ ('one',1),('two',2),('three',3) ] ) ) # 可迭代对象方式来构造字典
# 返回:{'two': 2, 'one': 1, 'three': 3}
print(dict(zip(["1","2","3"],["a","b","c"]))) # 映射函数方式来构造字典
# 返回:{'2': 'b', '3': 'c', '1': 'a'}
10. dir()函数不带参数时,返回当前范围内的变量、方法和定义的类型列表;带参数时,返回参数的属性、方法列表。文章源自玩技e族-https://www.playezu.com/26311.html
print( dir() ) # 获得当前模块的属性列表 # 返回:['__builtins__', '__cached__', '__doc__', '__file__', '__loader__', '__name__', '__package__', '__spec__'] print( dir([]) ) # 查看列表的方法 # 返回:['__add__', '__class__', '__contains__', '__delattr__', '__delitem__', '__dir__', '__doc__', '__eq__', '__format__', '__ge__', '__getattribute__', '__getitem__', '__gt__', '__hash__', '__iadd__', '__imul__', '__init__', '__iter__', '__le__', '__len__', '__lt__', '__mul__', '__ne__', '__new__', '__reduce__', '__reduce_ex__', '__repr__', '__reversed__', '__rmul__', '__setattr__', '__setitem__', '__sizeof__', '__str__', '__subclasshook__', 'append', 'clear', 'copy', 'count', 'extend', 'index', 'insert', 'pop', 'remove', 'reverse', 'sort']
11. divmod() 函数把除数和余数运算结果结合起来,返回一个包含商和余数的元组(商x,余数y)。文章源自玩技e族-https://www.playezu.com/26311.html
print( divmod(5,2) ) # 返回:(2, 1) print( divmod(5,1) ) # 返回:(5, 0) print( divmod(5,3) ) # 返回:(1, 2)
12. enumerate() 函数用于将一个可遍历的数据对象(如列表、元组或字符串)组合为一个索引序列,同时列出数据和数据下标,一般用在 for 循环当中。python 2.3. 以上版本可用,2.6 添加 start 参数。文章源自玩技e族-https://www.playezu.com/26311.html
1 seasons = ['spring', 'summer', 'fall', 'winter'] 2 print(list(enumerate(seasons))) # 返回:[(0, 'spring'), (1, 'summer'), (2, 'fall'), (3, 'winter')]
1 print(list(enumerate(seasons, start=1)) ) # 下标从 1 开始 # 返回:[(1, 'spring'), (2, 'summer'), (3, 'fall'), (4, 'winter')]
13. eval() 函数用来执行一个字符串表达式,并返回表达式的值。文章源自玩技e族-https://www.playezu.com/26311.html
print(eval('3 * 2')) # 6
1 x = 7
2 print(eval('3 x')) # 10
14. exec() 执行储存在字符串或文件中的python语句,相比于eval,exec可以执行更复杂的python代码。文章源自玩技e族-https://www.playezu.com/26311.html
exec("print('hello world')") # 执行简单的字符串
# hello world
exec("for i in range(5): print('iter time is %d'%i)") # 执行复杂的for循环
# iter time is 0
# iter time is 1
# iter time is 2
# iter time is 3
# iter time is 4
15. filter()用于过滤序列,过滤掉不符合条件的元素,返回一个迭代器对象,可用list()来转换为列表。文章源自玩技e族-https://www.playezu.com/26311.html
注意: filter()接收两个参数,第一个为函数,第二个为序列,序列的每个元素作为参数传递给函数进行判断,然后返回true或 false,最后将返回 true 的元素放到新列表中。文章源自玩技e族-https://www.playezu.com/26311.html
res = filter(lambda n:n>5,range(10)) # 过滤掉0-9中不符合n>5的数据
for i in res: # 循环打印符合n>5的数据
print(i)
# 5
# 6
# 7
# 8
# 9
16. format()是一种格式化字符串的函数 ,基本语法是通过 {} 和 : 来代替以前的 % 。format 函数可以接受不限个参数,位置可以不按顺序。文章源自玩技e族-https://www.playezu.com/26311.html
# 位置映射
print( "{}{}".format('a','1') )
# a1
print('name:{n},url:{u}'.format(n='alex',u='www.xxxxx.com'))
# name:alex,url:www.xxxxx.com
# 元素访问
print( "{0[0]},{0[1]}".format(('baidu','com')) ) # 按顺序
# baidu,com
print( "{0[2]},{0[0]},{0[1]}".format(('baidu','com','www')) ) # 不按顺序
# www,baidu,com
17. float() 函数用于将整数和字符串转换成浮点数。文章源自玩技e族-https://www.playezu.com/26311.html
print(float(1))
# 1.0
print(float(0.1))
# 0.1
print(float('123'))
# 123.0
18. frozenset() 返回一个冻结的集合(一个无序的不重复元素序列),冻结后集合不能再添加或删除任何元素。文章源自玩技e族-https://www.playezu.com/26311.html
1 a = frozenset(range(10)) # 先创建一个冻结集合
2 print(a)
3 # frozenset({0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9})
4
5 del a[0] # 试图删除冻结集合a中的元素,报错
6 # typeerror: 'frozenset' object doesn't support item deletion
1 b = frozenset("happy") # 将字符串转换成一个集合
2 print(b)
3 # frozenset({'a', 'h', 'p', 'y'}) # 无序不重复
1 c = frozenset() # 创建一个空集合 2 print(c) 3 # frozenset() # 如果不提供任何参数,默认会生成空集合
19. globals() 函数会以字典格式返回当前位置的全部全局变量。文章源自玩技e族-https://www.playezu.com/26311.html
print(globals()) # globals 函数返回一个全局变量的字典,包括所有导入的变量。
# {'__file__': 'c:/users/administrator/pycharmprojects/test/day4/内置函数-globals().py', '__spec__': none, '__doc__': none, '__package__': none,
'a': 'append', '__cached__': none, '__loader__': <_frozen_importlib_external.sourcefileloader object at 0x0000000000666b00>,
'__builtins__': , '__name__': '__main__'}
20. hasattr() 函数用于判断对象是否包含对应的属性。如果对象有该属性返回 true,否则返回 false。文章源自玩技e族-https://www.playezu.com/26311.html
1 class t: 2 a = 1 3 b = 2 4 c = 3 5 6 p = t() 7 print(hasattr(p,'a')) # true 8 print(hasattr(p,'b')) # true 9 print(hasattr(p,'x')) # false
21. hash() 用于获取一个对象(数字或者字符串等)的哈希值。不能直接应用于 list、set、dictionary。文章源自玩技e族-https://www.playezu.com/26311.html
注意:在 hash() 对对象使用时,所得的结果不仅和对象的内容有关,还和对象的 id(),也就是内存地址有关。文章源自玩技e族-https://www.playezu.com/26311.html
print(hash(1)) # 1
print(hash(20000)) # 20000
print(hash('123')) # -6436280630278763230
print(hash('ab12')) # 5468785079765213470
print(hash('ab12')) # 5468785079765213470
22. help() 函数用于查看函数或模块用途的详细说明。文章源自玩技e族-https://www.playezu.com/26311.html
help('sys') # 查看 sys 模块的帮助
help('str') # 查看 str 数据类型的帮助
a = [1,2,3] help(a) # 查看列表 list 帮助信息 help(a.append) # 显示list的append方法的帮助
23. hex() 函数用于将一个整数转换为十六进制数。返回一个字符串,以0x开头。文章源自玩技e族-https://www.playezu.com/26311.html
print(hex(1)) # 0x1 print(hex(-256)) # -0x100 print(type(hex(-256))) #
24. id()函数用于获取对象的内存地址。文章源自玩技e族-https://www.playezu.com/26311.html
a = "123" # 字符串
print(id(a)) # 13870392
b = [1,2,3] # 列表
print(id(b)) # 7184328
c = {'num1':1,'num2':2,'num3':3} # 字典
print(id(c)) # 6923656
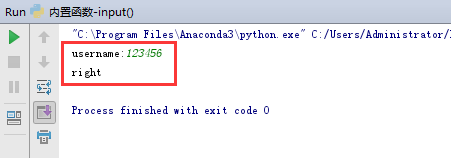
25. input() 函数接受一个标准输入数据,返回为 string 类型。这个函数是最最常用的了。在python3.x中 raw_input() 和 input() 进行了整合,仅保留了input( )函数。文章源自玩技e族-https://www.playezu.com/26311.html
a = '123456'
b = input("username:")
if b == a : # 如果b的输入数据等于a存储的数据,打印”right“
print("right")
else: # 否则打印”wrong“
print("wrong")
![]() 文章源自玩技e族-https://www.playezu.com/26311.html
文章源自玩技e族-https://www.playezu.com/26311.html
26. int() 函数用于将一个字符串或数字转换为整型。文章源自玩技e族-https://www.playezu.com/26311.html
print(int()) # 不传入参数时,得到结果0
print(int(0.5)) # 去掉小数部分,得到结果0
print(int(3)) # 得到结果3
print(int('0xa',16)) # 十六进制数“0xa”转换成十进制整数,得到结果10
print(int('00010',2)) # 二进制数“00010”转换成十进制整数,得到结果2
27. isinstance() 函数来判断一个对象是否是一个已知的类型,返回布尔值。类似 type()。文章源自玩技e族-https://www.playezu.com/26311.html
a = 2 print(isinstance(a,int)) # true print(isinstance(a,str)) # false print(isinstance(a,(str,tuple,dict))) # false print(isinstance(a,(str,tuple,int))) # 是元组其中的一个则返回true
- isinstance() 与 type() 区别:
type() 不会认为子类是一种父类类型,不考虑继承关系。 isinstance() 会认为子类是一种父类类型,考虑继承关系。 如果要判断两个类型是否相同推荐使用 isinstance()。 示例:
1 class a: 2 pass 3 4 class b(a): 5 pass 6 7 print(isinstance(a(),a)) # true 8 print( type(a()) == a ) # true 9 10 print(isinstance(b(),a)) # true 11 print( type(b()) == a ) # false --type()不考虑继承关系
28. issubclass()用于判断参数class是否是类型参数classinfo的子类,是则返回true,否则返回false。文章源自玩技e族-https://www.playezu.com/26311.html
语法:issubclass(class,classinfo)。文章源自玩技e族-https://www.playezu.com/26311.html
1 class a: 2 pass 3 class b(a): # b继承了a,即b是a的子类 4 pass 5 6 print(issubclass(a,b)) # 判断 a 是 b 的子类? 7 # false 8 print(issubclass(b,a)) # 判断 b 是 a 的子类? 9 # true
29. iter() 函数用来生成迭代器。list、tuple等都是可迭代对象,我们可以通过iter()函数获取这些可迭代对象的迭代器,然后可以对获取到的迭代器不断用next()函数来获取下条数据。iter()函数实际上就是调了可迭代对象的 __iter__ 方法。文章源自玩技e族-https://www.playezu.com/26311.html
# 注意:当已经迭代完最后一个数据之后,再次调用next()函数会抛出 stopiteration的异常,来告诉我们所有数据都已迭代完成。文章源自玩技e族-https://www.playezu.com/26311.html
1 it = [1,2,3] 2 it_list = iter(it) 3 4 print(next(it_list)) 5 # 1 6 print(next(it_list)) 7 # 2 8 print(next(it_list)) 9 # 3 10 print(next(it_list)) 11 # stopiteration
30. len() 方法返回对象(字符、列表、元组等)长度或元素个数。文章源自玩技e族-https://www.playezu.com/26311.html
# len()方法返回对象(字符、列表、元组等)长度或元素个数。
print(len('1234')) # 字符串,返回字符长度4
print(len(['1234','asd',1])) # 列表,返回元素个数3
print(len((1,2,3,4,50))) # 元组,返回元素个数5
print(len(12)) # 注意:整数类型不适用,否则报错
# typeerror: object of type 'int' has no len()
31. list() 方法用于将元组转换为列表。文章源自玩技e族-https://www.playezu.com/26311.html
注:元组与列表是非常类似的,区别在于元组的元素值不能修改,元组是放在括号中,列表是放于方括号中。文章源自玩技e族-https://www.playezu.com/26311.html
print( list((1,2,3))) # [1, 2, 3]
32. map()接收函数f和list,并通过把函数f依次作用在list的每个元素上,得到一个新的list并返回。文章源自玩技e族-https://www.playezu.com/26311.html
1 res = map(lambda n: n*2,[0,1,2,3,4,5]) # 使用 lambda 匿名函数 2 for i in res: 3 print(i) 4 5 # 返回以下数据: 6 # 0 7 # 2 8 # 4 9 # 6 10 # 8 11 # 10
1 # 提供了两个列表,对相同位置的列表数据进行相加 2 3 a = map(lambda x,y : x y,[1,2,3,4,5],[2,4,6,8,10]) 4 for i in a: 5 print(i) 6 7 # 返回以下数据: 8 # 3 9 # 6 10 # 9 11 # 12 12 # 15
33. max()函数返回给定参数的最大值,参数可以为序列。文章源自玩技e族-https://www.playezu.com/26311.html
print("max(10,20,30):" , max(10,20,30) )
# max(10,20,30): 30
print("max(10,-2,3.4):" , max(10,-2,3.4) )
# max(10,-2,3.4): 10
print("max({'b':2,'a':1,'c':0}):" , max({'b':2,'a':1,'c':0}) ) # 字典,默认按key排序
# max({'b':2,'a':1,'c':0}): c
34. min()函数返回给定参数的最小值,参数可以为序列。文章源自玩技e族-https://www.playezu.com/26311.html
print("min(10,20,30):" , min(10,20,30) )
# min(10,20,30): 10
print("min(10,-2,3.4):" , min(10,-2,3.4) )
# min(10,-2,3.4): -2
print("min({'b':2,'a':1,'c':0}):" , min({'b':2,'a':1,'c':0}) ) # 字典,默认按key排序
# min({'b':2,'a':1,'c':0}): a
35. next() 返回迭代器的下一个项目。文章源自玩技e族-https://www.playezu.com/26311.html
1 # 首先获得iterator对象: 2 it = iter([1,2,3,4,5]) 3 4 # 循环: 5 while true: 6 try: 7 # 获得下一个值: 8 x = next(it) 9 print(x) 10 except stopiteration: 11 break 12 # 遇到stopiteration就退出循环
36. oct() 函数将一个整数转换成八进制字符串。文章源自玩技e族-https://www.playezu.com/26311.html
print( oct(10) ) # 0o12 print( oct(255) ) # 0o377 print( oct(-6655) ) # -0o14777
37. open() 函数用于打开一个文件,创建一个 file 对象,相关的方法才可以调用它进行读写。文章源自玩技e族-https://www.playezu.com/26311.html
f = open("test1.txt","w",encoding="utf-8") # 创建一个file
print(f.write("abc"))
f = open("test1.txt","r",encoding="utf-8") # 读取文件数据
print(f.read())
38. ord()函数是chr()的配对函数,它以一个字符(长度为1的字符串)作为参数,返回对应的ascii数值,或者unicode数值,如果所给的 unicode 字符超出了定义范围,则会引发一个 typeerror 的异常。文章源自玩技e族-https://www.playezu.com/26311.html
# 把字符 b(长度为1的字符串)作为参数在ascii码中对应的字符打印出来
print( ord('b') ) # 返回:98
print( ord('%') ) # 返回:37
39. pow()函数返回x的y次方的值。文章源自玩技e族-https://www.playezu.com/26311.html
注意:pow()通过内置的方法直接调用,内置方法会把参数作为整型,而 math 模块则会把参数转换为 float。文章源自玩技e族-https://www.playezu.com/26311.html
# 通过内置的方法直接调用 print( pow(2,2) ) # 2的二次方 # 4 print( pow(2,-2) ) # 2的负二次方 # 0.5
1 # 导入math模块 2 3 import math 4 5 print(math.pow(3,2)) # 3的负二次方 6 # 9.0
40. print()用于打印输出,最常见的一个函数。print 在python3.x是一个函数,但在python2.x版本只是一个关键字。文章源自玩技e族-https://www.playezu.com/26311.html
print( abs(-45) ) # 45
print("hello world!") # hello world!
print([1,2,3]) # [1, 2, 3]
41. range() 函数可创建一个整数列表,一般用在 for 循环中。语法:range(start, stop[, step])文章源自玩技e族-https://www.playezu.com/26311.html
for i in range(10):
print(i) # 依次打印数字0-9
for a in range(0,10,2): # 步长为2
print(a) # 打印0,2,4,6,8
for b in range(10, 0, -2): # 步长为-2
print(b) # 打印10,8,6,4,2
42. reduce() 函数会对参数序列中元素进行累积。在python3 ,reduce()被放置在functools模块里,如果想要使用它,需要先引入functools模块。文章源自玩技e族-https://www.playezu.com/26311.html
import functools a = functools.reduce(lambda x,y:x y,[1,2,3]) print(a) # 6 , 即从1加到3 b = functools.reduce(lambda x,y:x y,range(10)) print(b) # 45 , 即从0加到9
43. repr() 函数将对象转化为供解释器读取的形式。返回一个对象的 string 格式文章源自玩技e族-https://www.playezu.com/26311.html
r = repr((1,2,3)) print( r ) # (1, 2, 3) print( type(r) ) #dict = repr({'a':1,'b':2,'c':3}) print( dict ) # {'c': 3, 'a': 1, 'b': 2} print( type(dict) ) #
44. reversed() 函数返回一个反转的迭代器。 reversed(seq)要转换的序列,可以是 tuple, string, list 或 range文章源自玩技e族-https://www.playezu.com/26311.html
rev = reversed( [1,2,3,4,5] ) # 列表
print(list(rev))
# [5, 4, 3, 2, 1]
rev1 = reversed( "school" ) # 元组
print(tuple(rev1))
# ('l', 'o', 'o', 'h', 'c', 's')
rev2 = reversed(range(10)) # range
print(list(rev2))
# [9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0]
45. round() 方法返回浮点数x的四舍五入值。(除非对精确度没什么要求,否则尽量避开用round()函数)文章源自玩技e族-https://www.playezu.com/26311.html
print( round(4.3)) # 只有一个参数时,默认保留到整数 # 4 print( round(2.678,2)) # 保留2位小数 # 2.68 print( round(5/3,3)) # 运算表达式并保留3位小数 # 1.667
46. set() 函数创建一个无序不重复元素集,可进行关系测试,删除重复数据,还可以计算交集、差集、并集等。文章源自玩技e族-https://www.playezu.com/26311.html
1 a = set('school')
2 print(a) # 重复的被删除,得到结果:{'o', 'c', 's', 'l', 'h'}
1 b = set([1,2,3,4,5])
2 c = set([2,4,6,8,10])
3
4 print(b & c) # 交集,得到结果为{2, 4}
5 print(b | c) # 并集,得到结果为{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 10}
6 print(b - c) # 差集,得到结果为{1, 3, 5}
47. slice() 函数实现切片对象,主要用在切片操作函数里的参数传递。文章源自玩技e族-https://www.playezu.com/26311.html
a = slice("school")
print(a) # slice(none, 'school', none)
48. sorted() 函数对所有可迭代的对象进行排序(默认升序)操作。文章源自玩技e族-https://www.playezu.com/26311.html
# 对列表进行排序
print(sorted([1,2,5,30,4,22])) # [1, 2, 4, 5, 22, 30]
# 对字典进行排序
dict = {23:42,1:0,98:46,47:-28}
print( sorted(dict) ) # 只对key排序
# [1, 23, 47, 98]
print( sorted(dict.items()) ) # 默认按key进行排序
# [(1, 0), (23, 42), (47, -28), (98, 46)]
print( sorted(dict.items(),key=lambda x:x[1]) ) # 用匿名函数实现按value进行排序
# [(47, -28), (1, 0), (23, 42), (98, 46)]
# 利用key进行倒序排序 test1 = [1,2,5,30,4,22] r_list = sorted(test1,key=lambda x:x*-1) print(r_list) # [30, 22, 5, 4, 2, 1] # 要进行反向排序,也可以通过传入第三个参数 reverse=true: test2 = [1,2,5,30,4,22] print(sorted(test2,reverse=true)) # [30, 22, 5, 4, 2, 1]
49. str() 函数将对象转化为string格式。文章源自玩技e族-https://www.playezu.com/26311.html
1 a = str((1,2,3)) 2 print(a) # 打印a,得到结果(1, 2, 3) 3 print(type(a)) # 打印a的类型,得到结果
50. sum()函数对参数进行求和计算。文章源自玩技e族-https://www.playezu.com/26311.html
print( sum([1,2,3]) ) # 6 print( sum([1,2,3],4) ) # 列表计算总和后再加4,得到结果10 print( sum( (1,2,3),4 ) ) # 元组计算总和后再加4,得到结果10
51. tuple()函数将列表转换为元组。文章源自玩技e族-https://www.playezu.com/26311.html
# 注:元组与列表是非常类似的,区别在于元组的元素值不能修改,元组是放在括号中,列表是放于方括号中。文章源自玩技e族-https://www.playezu.com/26311.html
print( tuple([1, 2, 3])) # (1,2,3)
52. type() 函数如果你只有第一个参数则返回对象的类型,三个参数返回新的类型对象。文章源自玩技e族-https://www.playezu.com/26311.html
print(type(1)) #print(type("123")) # print(type([123,456])) # print(type( (123,456) ) ) # print(type({'a':1,'b':2}) ) #
53. zip() 函数用于将可迭代的对象作为参数,将对象中对应的元素打包成一个个元组,然后返回由这些元组组成的对象,这样做的好处是节约了不少的内存。可以使用 list() 转换来输出列表。如果各个迭代器的元素个数不一致,则返回列表长度与最短的对象相同。利用 * 号操作符,可以将元组解压为列表。文章源自玩技e族-https://www.playezu.com/26311.html
1 a = [1,2,3] 2 b = [4,5,6] 3 c = [7,8,9,10] 4 5 for i in zip(a,b): 6 print(i) 7 8 # 返回结果: 9 # (1, 4) 10 # (2, 5) 11 # (3, 6) 12 13 print(list(zip(a,b))) # list() 转换为列表 14 # [(1, 4), (2, 5), (3, 6)] 15 16 print(list(zip(b,c))) # 元素个数与最短的列表一致 17 # [(4, 7), (5, 8), (6, 9)] 18 19 a1,a2 = zip(*zip(a,b)) # 用zip(*)解压 20 print(list(a1)) # [1, 2, 3] 21 print(list(a2)) # [4, 5, 6]
54. __import__() 函数用于动态加载类和函数。如果一个模块经常变化就可以使用 __import__() 来动态载入。文章源自玩技e族-https://www.playezu.com/26311.html
__import__('decorator')
# 返回结果如下:
# in the bar
# the func run time is 3.000171661376953
# 首先获得iterator对象:
it = iter([1,2,3,4,5])
# 循环:
while true:
try:
# 获得下一个值:
x = next(it)
print(x)
except stopiteration:
break
# 遇到stopiteration就退出循环
文章源自玩技e族-https://www.playezu.com/26311.html 免责声明:本文内容来自用户上传并发布或网络新闻客户端自媒体,玩技博客仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如发现本站有涉嫌抄袭侵权/违法违规的内容,请联系删除。

评论